The essential takeaway: Edge AI executes machine learning directly on local devices instead of relying on distant cloud servers. By analyzing data where it is created, this technology eliminates lag and significantly enhances privacy. It empowers smart gadgets and autonomous vehicles to make split-second decisions independently, ensuring reliability even when the internet connection drops.
Have you ever wondered why your smart home sometimes feels a bit sluggish or worried about your private footage traveling across the web for analysis? That is precisely the problem edge ai fixes by moving intelligence from remote data centers directly to your local devices for immediate processing. We are going to explore how this local approach grants your electronics near-instant decision-making powers and why it is the best move for keeping your sensitive data under your own roof.
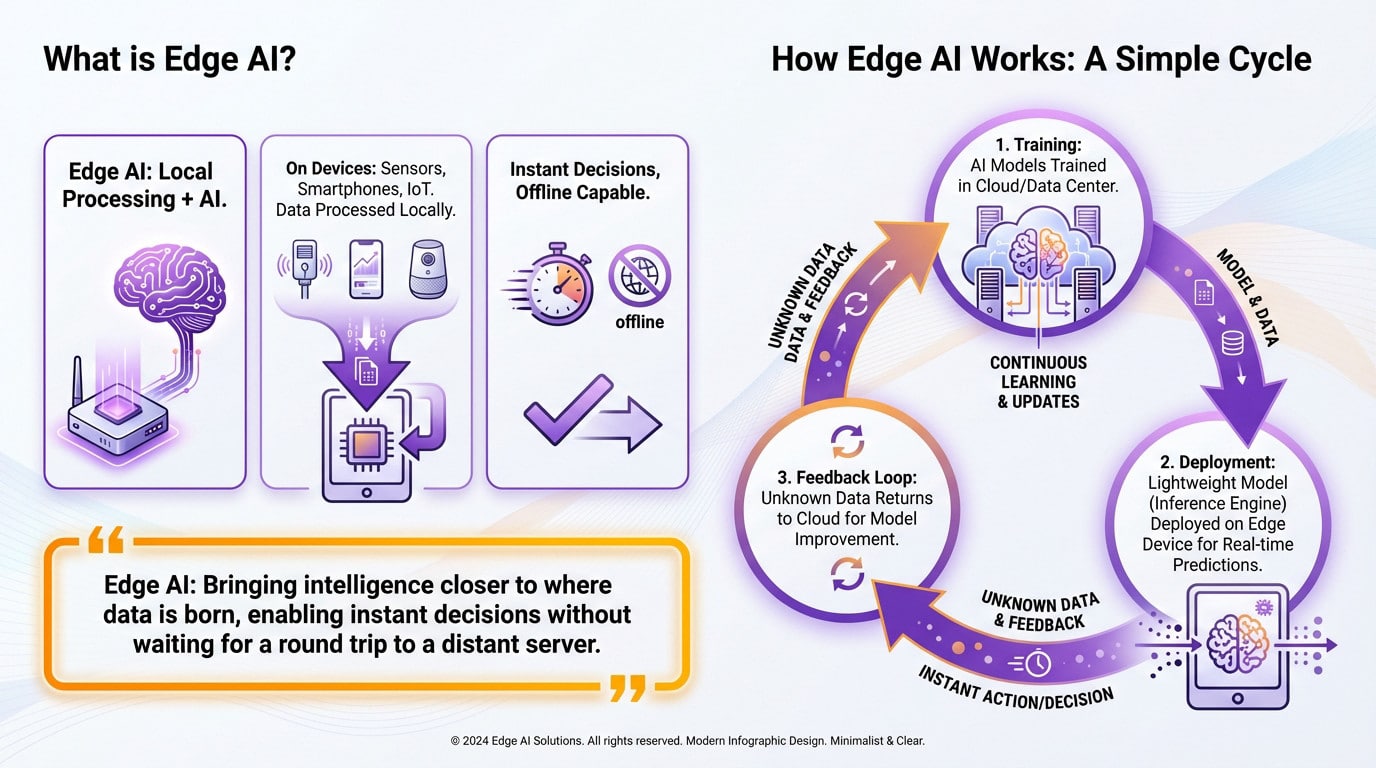
What is edge ai anyway?
Let’s cut through the noise. Edge AI isn’t just another buzzword; it is a fundamental shift in where machines do their thinking, moving intelligence from distant servers right into your hand.
Defining AI at the Network’s Edge
At its heart, this technology is simply the marriage of edge computing and intelligence artificielle. The concept is straightforward: the heavy math happens locally on the device, not in the cloud. You stop outsourcing the thinking.
We are talking about running intelligence directly on sensors, smartphones, and IoT gadgets. This setup lets you process data locally, right at the source where it is actually generated, without needing a long trip to a remote server. The action stays here.
The result is split-second decision-making that works perfectly, even when the internet goes down.
How It Actually Works: A Simple Cycle
It starts with the heavy lifting called training. Massive neural networks learn from mountains of data, usually inside a powerful cloud infrastructure or a centralized data center.
Once the brain is smart enough, we shrink it down. A lean version, the inference engine, gets deployed straight to your edge device. Now, it makes predictions in real-time without phoning home.
If the device sees something weird it doesn’t recognize, it flags it. That specific data goes back to the cloud to make the model smarter.
The Core Idea in a Nutshell
Think of a security camera. Instead of streaming hours of empty hallway footage to the cloud, a camera with edge ai spots the intruder itself and only sends the alert. It’s faster, and frankly, much more private.
Edge AI isn’t about replacing the cloud; it’s about bringing intelligence closer to where data is born, enabling instant decisions without waiting for a round trip to a distant server.
Edge vs. Cloud: A Partnership, Not a Fight
Now that we have the basics, let’s kill a common myth right now: Edge AI isn’t here to replace the Cloud. Actually, they are just two sides of the same coin.
Understanding Their Distinct Roles
Think of Cloud AI as the gym. It has massive computing power and storage, which is absolutely necessary to train complex models using terabytes of data. It is where the heavy lifting happens to build the brain.
On the flip side, we have edge ai. This is the playing field. It focuses entirely on real-time inference, applying that trained model to make fast predictions right on the device, exactly where the action is happening.
A Tale of Two AIs: A Head-to-Head Comparison
You might wonder how they stack up against each other. This table visualizes the specific strengths and weaknesses of each approach, so you can see exactly where they differ.
| Feature | Edge AI | Cloud AI |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Low (milliseconds, on-device processing) | High (dependent on network connection to remote servers) |
| Network Bandwidth | Low (minimal data transmission) | High (requires constant data upload/download) |
| Computing Power | Limited (constrained by device hardware) | Virtually Unlimited (access to massive data centers) |
| Data Privacy & Security | High (data processed and stored locally) | Lower (sensitive data transmitted over the network) |
| Offline Capability | Yes (can operate without an internet connection) | No (requires constant connectivity) |
The Hybrid Architecture: Better Together
The smartest approach is usually a hybrid one. The cloud manages the heavy training and retraining of models, while the edge handles the fast, daily execution of tasks. It works because each does what it does best.
Picture a head chef creating a complex recipe; that is the cloud. Then you have the line cook, the edge, executing that recipe perfectly and quickly in the kitchen.
This synergy between edge and cloud is the keystone of many modern applications. From self-driving cars to smart factories, they all rely on this partnership.
The Real-World Perks: Why You Should Care
Instantaneous Response: Killing Latency
Latency is the absolute enemy of critical applications. It is simply the lag between collecting data and getting a response. Edge AI eliminates this delay by crunching numbers right on the spot. Speed is everything here.
Take a self-driving car; it cannot wait for cloud servers to decide when to brake. That decision must be immediate to prevent a crash. This real-time analysis is vital, much like the need for reducing latency in smart warehouses.
Your Data Stays With You: A Win for Privacy
Let’s be honest about privacy risks today. Sending personal data to distant external servers always carries a massive security risk. Fortunately, Edge AI completely changes this dangerous game.
By processing sensitive info—like security camera footage or health stats—locally, we drastically minimize exposure. You keep control over what matters most. Data privacy becomes natively reinforced without any extra effort required from users.
With Edge AI, sensitive information doesn’t need to travel. It’s analyzed where it’s created, significantly reducing the attack surface for data breaches and enhancing user trust.
The Core Benefits at a Glance
The advantages are multiple and they reinforce each other beautifully. This creates a powerful and efficient ecosystem.
- Reduced latency: For real-time responses and immediate feedback.
- Enhanced data privacy: By processing sensitive data on-device instead of sending it to the cloud.
- Lower bandwidth usage: Drastically cutting down the amount of data that needs to be transmitted, which also reduces costs.
- Improved reliability: Applications can function even with an unstable or non-existent internet connection.
- Better scalability: Adding new devices doesn’t proportionally increase the load on central cloud resources.
Edge AI in Action: From Your Home to the Factory Floor
Enough theory. Let’s see where this tech is already making waves. You would be surprised to see just how much edge ai is already present all around us.
Smart Devices Getting Smarter
Think about your living room right now. Voice assistants answer instantly because they process audio locally, not on a distant server. Video doorbells recognize faces without uploading the feed. Even smart thermostats learn your daily habits to adjust the heat before you walk in.
It gets personal with health tech. Wearables like smartwatches analyze your heart rate continuously on your wrist. If they detect a sudden fall, they alert emergency services immediately. They do this life-saving work even without needing an active internet connection.
Transforming Key Industries
Now, look at the factory floor. This is where predictive maintenance saves serious money. Sensors attached to machines analyze vibrations and temperatures in real-time. They spot a breakdown days before it happens, preventing costly downtime without waiting for a human to check.
Retail is catching up fast, too. Smart carts scan your groceries as you drop them in, skipping the checkout line entirely. Cameras analyze customer flow to help managers organize aisles better. To discover other use cases, you can explore our AI blog.
The Future of Mobility and Security
Self-driving cars are the ultimate test here. A vehicle must make hundreds of split-second decisions based on sensor data. Relying on a slow cloud connection here isn’t just annoying. It is impossible without ultra-fast, onboard AI processing.
Finally, consider modern security systems. Advanced computer vision on cameras can detect suspicious behavior in real-time. They process the feed locally instead of clogging the network. This avoids sending hours of useless video footage to a server just to find nothing.
The Nuts and Bolts: Deploying AI on Tiny Devices
It sounds great on paper, but how do you actually shove a massive digital brain onto a chip the size of a fingernail? That’s where the real engineering headache begins.
The Challenge of Limited Resources
You can’t just drag and drop a massive cloud model onto a thermostat. These edge devices have tiny batteries and limited memory compared to a server farm. It’s like trying to park a semi-truck in a compact spot. The hardware simply refuses to cooperate.
So, engineers have to shrink these AI models down without making them stupid. It becomes a high-stakes balancing act between speed and accuracy. If you cut too much, the system fails to recognize anything useful.
Making Models Smaller and Faster
This is where the magic happens, specifically through two main techniques. We use pruning to trim away useless connections, much like gardening a bonsai tree. Then there is quantization, which forces the math to use simpler numbers. It makes the heavy lifting manageable.
The end result is a lean, “light” model ready for action. It runs fast on specialized hardware like NPUs or integrated GPUs found in modern chips. This allows edge ai to process data instantly without lagging. Speed is the only currency here.
Tools of the Trade for Developers
Luckily, developers don’t have to code this from scratch. There is a whole arsenal of tools waiting for them.
You might be surprised by how accessible these frameworks have become for engineers. Instead of reinventing the wheel, they rely on established ecosystems to handle the heavy lifting of optimization and deployment on specific hardware.
- TensorFlow Lite & PyTorch Mobile: Lightweight versions of popular AI frameworks, designed specifically for mobile and embedded devices.
- MediaPipe: A Google framework for building cross-platform multimodal applied ML pipelines.
- Edge AI Studio / LiteRT: Specific toolkits from hardware manufacturers (like Texas Instruments) to optimize models for their chips.
- Keras & JAX: High-level APIs and libraries that help in building and training models that can then be converted for edge deployment.
Edge AI isn’t just a buzzword; it’s reshaping how our gadgets “think.” By moving intelligence from distant servers to the device in your hand, we gain speed, privacy, and reliability. The cloud isn’t going anywhere, but the future is clearly happening right here, at the edge—smart toasters and all.




