Why can your prompt change everything in AI? The quality of your results on an AI, such as ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, etc., will depend directly on your ability to formulate good prompts! Without precise instructions, even the most advanced chatbots produce fuzzy, biased or even completely ineffective responses. That’s where Prompt Engineering comes in!
Prompt Engineering is the methodology for structuring your prompts. It’s how you formulate effective prompts that will help you obtain relevant responses from AI. And it has now become a real strategic skill in many professional fields, beyond digital marketing, content creators or data analysts…
This guide will help you understand how AI works, so you can write the best prompts and save precious time!
Defining Prompt Engineering: more than just instructions
Before looking at the methodology for making effective prompts, let’s consider the definition of an AI prompt: an AI prompt is an instruction or set of instructions given to an artificial intelligence (AI) to perform a specific task. It is the starting point for the AI to generate responses or creations accordingly.
That’s why the prompt given to an AI can change everything! Prompt Engineering is the art of formulating the right instructions to get what you want from an AI. And these instructions can vary depending on the type of AI and the objective being pursued (in this case, generative AI).
To prevent the AI from getting lost in generic or useless responses, it needs precise guidelines. Even the most advanced models, such as ChatGPT or Claude, need this: they are powerful engines… and you remain the driver.
To make a good prompt: the more qualitative you are, the more meticulous and relevant the AI will be.
Prompt Engineering: the structure of an effective prompt
How to make an effective prompt? The typical structure of an AI prompt is Role + Task + Context + Constraints + Format.
A good prompt isn’t just a well-turned question. It’s a human-machine communication strategy, where every word counts:
- Role: “You’re a B2B marketing expert…”
- Task: “…your mission is to write a prospecting email…”
- Context: “…for a SaaS startup in cybersecurity…”
- Constraints: “…with a formal tone, no technical jargon, and a clear call-to-action.”
A good AI prompt is clear and precise: it tells you exactly what you want from the AI! The fun fact is that you can ask the AI to generate a prompt!
How does an AI like ChatGPT work, and why does it need a well-formulated prompt?
To make the most of ChatGPT or any other LLM (Large Language Model), you need to understand its basic mechanisms. Without this, even the best model will remain mute in the face of vague instructions.
The principles for understanding how an AI like ChatGPT works will be :
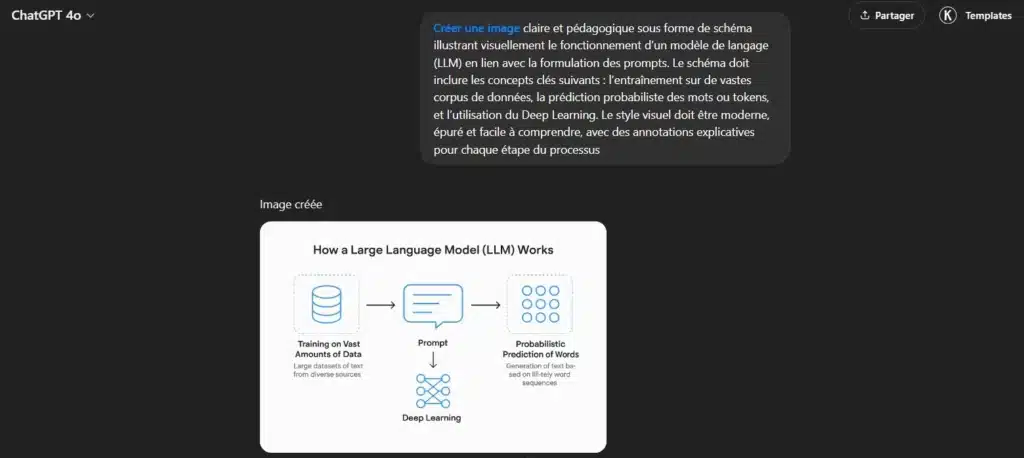
- Training on vast corpora: LLMs are exposed to billions, even trillions of words from a variety of sources (books, articles, online forums). This enables them to learn the relationships between words, grammatical structures, sentences and styles;
- Probabilistic prediction: when you interact with ChatGPT, it doesn’t look for an objective truth. Instead, it predicts the next most likely word based on the context provided. It is this mechanism that enables it to generate fluid text, so the initial formulation of your instructions (prompt) must be exhaustive;
- Deep Learning: at the heart of it all, deep neural networks analyze the nuances of language, innuendo and complex structures – without explicit human-coded rules. This is what makes these AIs capable of translating, writing, explaining or simulating natural conversations.

Advanced techniques for good AI prompts: methodology and strategy
Modularity: create adaptable template prompts
A template is a recoverable model that you can customize according to your needs. It can be reused for similar tasks, such as creating posts or professional emails. All you have to do is adjust the context or tone without too much thought.
Example of an IA prompt database
“As [Role], generate [Content type] on [Subject] respecting [Constraint “s]. Example: [1-2 examples]. “
Few-shot prompting: adding examples to your AI prompt
Few-shot prompting enables you to clarify the format and type of response expected, based on convincing examples. This involves integrating 2 to 4 examples into the prompt to help the AI better understand the task at hand.
Example of a few-shot AI prompt
“Analyzes the sentiment of the following customer reviews:
- ‘Impeccable service, fast delivery.’ → Positive
- ‘Disappointed by the quality of the product.’ → Negative
- ‘Good value for money, but lead times too long.’ → Mixed
Analysis now: ‘The application is useful, but buggy.'”*
Chain-of-thought prompting: guiding AI and its reasoning
To get a more structured and logical response from the AI, we’ll have to force it somewhat by getting it to break down its reasoning step by step. This is the definition of chain-of-thought prompting: instead of generating an immediate response, it details the steps leading to the conclusion.
The benefits are compelling, especially when you start to seriously doubt the AI’s answers: there are fewer logical errors, greater transparency in the process, and answers that are closer to human reasoning.
Chain-of-thought AI prompt example
Classic Prompt: “What’s the best customer acquisition strategy in 2025?”
Chain-of-thought optimized Prompt:
“Break down the different customer acquisition strategies that a startup could adopt in 2025. Analyze them one by one according to their cost, estimated ROI and difficulty of implementation, then suggest the most relevant one.”
In particular, you can specify the expected structure in the prompt, for example :
“Start by listing the options → analyze each option → synthesize the best solution with justification.”
A/B testing: comparing different prompts
A/B testing involves creating two or more versions of the same prompt (for example, “Prompt A” and “Prompt B”) and testing them simultaneously to assess which produces the best results. This method will enable you to quickly identify which is the most effective formulation for the given task.
In concrete terms, how do you proceed with A/B testing?
- Formulate several variants of a prompt by modifying a key element (tone, structure, context, etc.);
- Test them on real cases or similar data sets;
- Measure performance according to specific criteria: clarity, relevance, expected format, or user satisfaction;
Example of an AI prompt in A/B testing
Prompt A: “Explain the advantages of teleworking in list form.”
Prompt B: “Write a short article about the benefits of telecommuting with concrete examples.”
Analyze which of the two variants generates a response more in line with your expectations.
Finally, what is the ideal structure for an AI prompt?
With all these prompt writing techniques, how do you choose the best one? You don’t have to limit yourself to just one method; you can totally combine several methods! Let’s summarize the key information for making a good IA prompt:
- A clear role (e.g. expert, journalist, coach, etc.) ;
- 2 well-chosen examples;
- An instruction broken down into steps ;
- A format constraint (table, bullet points, summary…)
In particular, you can ask an AI to generate several answers to the question!
Prompt Engineering: tips and advice for writing prompts
To take Prompt Engineering one step further, keep these tips and advice in mind:
- Use precise action verbs: “analyze”, “summarize”, “compare”, “prioritize”;
- Integrate the message target: “for managers”, “for beginners”;
- Specify the expected output format: list, table, summary sheet… ;
- Avoid generalizations: be surgical in your instructions;
- Keep a “prompt book” by theme for your recurring models.
Case studies: examples of marketing-optimized prompts
| Use cases | Example of an optimized prompt | Expected result |
| Personalized e-mail | “Write an email to launch our organic range, with analysis of previous purchases + promo code 10OFF.” | Segmented message, emotional copy, clear CTA. |
| Social networking | “Offers the best coffee-themed Instagram slots + relevant hashtags.” | Planning optimized for peak engagement. |
| Lead generation | “List 50 qualified leads for [site], including company, position, contact information, industry.” | Ready-to-use file for prospecting. |
These prompts are taken from the PromptEngineeringGuide.ai prompt example site.
Common AI prompt errors
To get the result you want when querying an AI, we present a checklist to help you formulate your AI prompt:
- Clear objective?
- Strategic keywords included?
- Style and tone defined?
- Imposed output format?
- Enough examples?
- Too long? Too vague?
It’s best not to give too much information at once to an AI, in which case the model may become cognitive. So break it down into simple sub-components!
Here are some examples of poorly formulated AI prompts and how to improve them:
- “Make a post for social networks.” Which social network? What type of content? What objective? ;
- “Write an article about the environment.” : subject too broad, no indication of angle, length, audience, etc. ;
- “Make a code for a website.” What kind of website? What functionalities? Which programming language?
- “Answer this customer.” Which customer? What is his question or problem?
- “Handle this complaint.” What complaint? What’s the context?
How can you analyze and improve your AI prompts?
Finally, if you want to improve your prompts, you can have their performance measured. This will help you analyze relevance and consistency, always with a view to saving time. Note that most of these prompts generation and verification platforms are not free: PromptLayer.com, PromptBetter.com (free!), LangSmith.com.